SLTE v.101 Linearity / Reportable Range
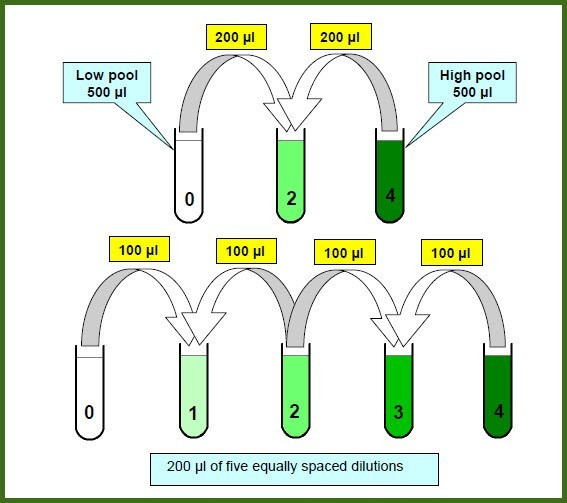
EXCEL File has Spreadsheets for 3, 4, 5, 6 Levels to Assess Analyte Linearity and Reportable Range
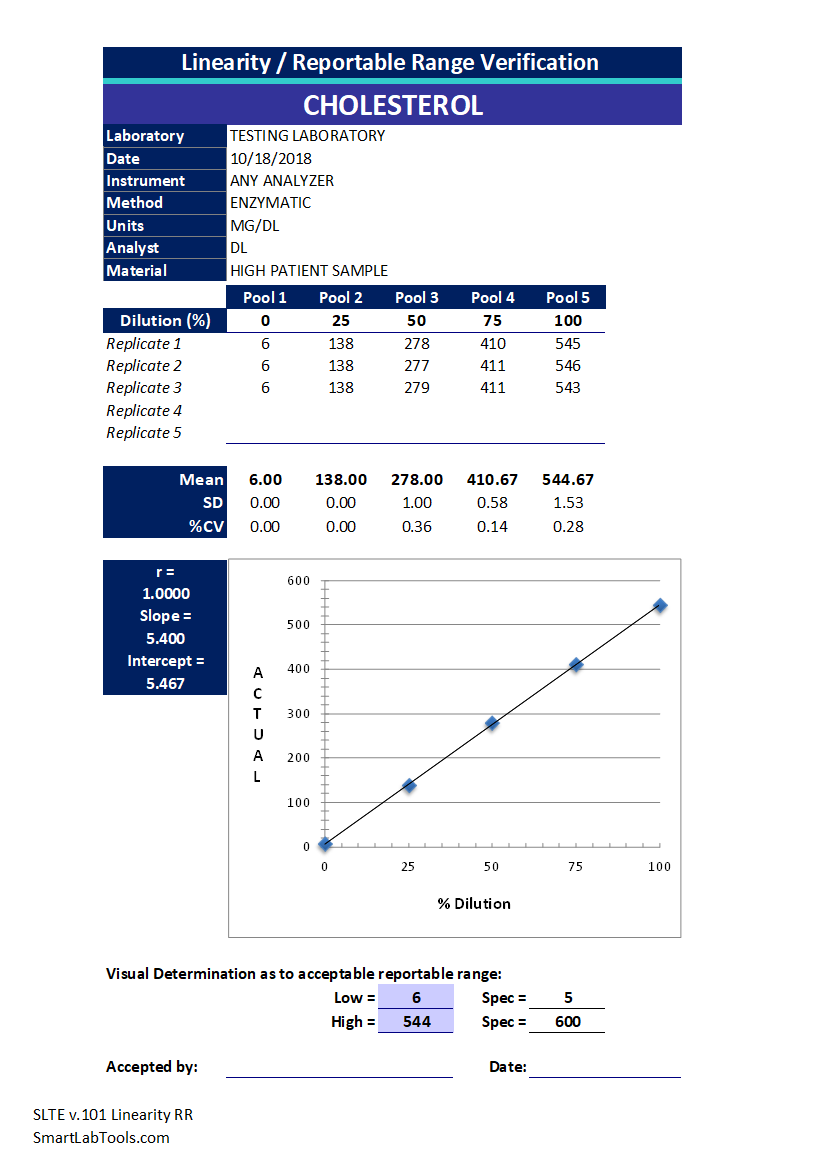
Linearity
Linearity is achieved when measured results are directly proportional to the concentration of the analyte in the test sample, within a given range.
Reportable Range
This is defined as the span of test result values over which the laboratory can establish or verify the accuracy of the instrument or test system measurement response. To determine how high and low test values can be and still be accurate, the laboratory needs to choose samples with known values at the highest and lowest levels of which the manufacturer claims accurate results can be produced by the test system. The laboratory may only report patient test results that fall within the verified levels. The reportable range can be expanded if the results are verified. Additionally, the laboratory must decide how to report results that are greater than the highest verified level or less than the lowest level.
Calibration Verification
Calibration verification is the assaying materials of known concentration in the same manner as patient samples to substantiate the instrument’s calibration throughout the reportable range for patient test results. If the calibration verification confirms that calibration settings are valid for a method, no further calibration actions are necessary. Calibration verification requires the use of materials with assayed values while verification of the reportable range does not.
References:
Verification of Performance Specifications
Reportable Range, Linearity & Calibration Verification